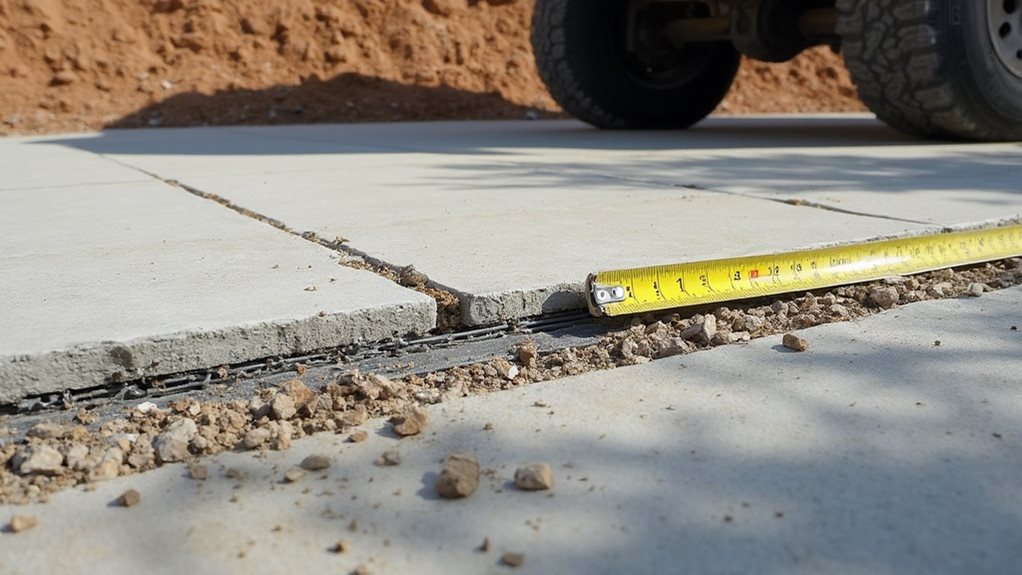

Concrete Driveways Load Capacity and Thickness Considerations
Concrete driveway specifications depend primarily on expected vehicle loads, with residential driveways typically requiring 4 inches thickness for standard passenger vehicles under 4,000 pounds. Commercial applications demand 6-8 inches thickness to accommodate vehicles up to 66,000 pounds, while proper soil preparation and reinforcement enhance load capacity. Climate conditions, soil stability, and regular maintenance influence durability, with quality installations lasting 25-30 years. Understanding these key factors guarantees ideal driveway performance through its lifetime.
Expert Highlights
- Standard residential driveways require 4-inch thickness for vehicles up to 4,000 pounds, while commercial driveways need 6-8 inches for heavier loads.
- Soil testing and proper site preparation with 95% compaction rate are essential for ensuring driveway stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Reinforcement options like steel rebar, wire mesh, or fiber technology enhance load capacity and extend driveway lifespan up to 30 years.
- Anticipated vehicle weight and traffic frequency determine thickness requirements, with heavy equipment needing 5-8 inches of concrete thickness.
- Quality concrete mix with 4,500 PSI compressive strength and proper water-cement ratios optimize load-bearing performance and durability.
Understanding Load Capacity Requirements for Different Vehicle Types

The load capacity requirements for different vehicle types represent a critical consideration when designing and constructing concrete driveways, as these specifications directly impact the structural integrity and longevity of the surface.
Proper load capacity specifications remain essential to driveway design, directly determining how well the concrete structure performs over time.
Standard passenger vehicles, typically weighing between 3,000 and 4,000 pounds, require minimal load-bearing capacity compared to larger vehicles.
Commercial trucks, recreational vehicles, and service vehicles demand substantially higher load capacities. Class 6 medium-duty trucks can weigh up to 26,000 pounds, while larger delivery vehicles may exceed 33,000 pounds when fully loaded.
Construction equipment, such as concrete mixers weighing approximately 66,000 pounds when loaded, necessitates the most robust driveway specifications.
These weight variations inform essential calculations for concrete thickness, reinforcement requirements, and sub-base preparation, ensuring the driveway meets both current needs and anticipated future use.
A properly installed gravel base layer provides crucial support for distributing heavy vehicle loads and preventing surface damage over time.
Key Factors That Determine Driveway Thickness
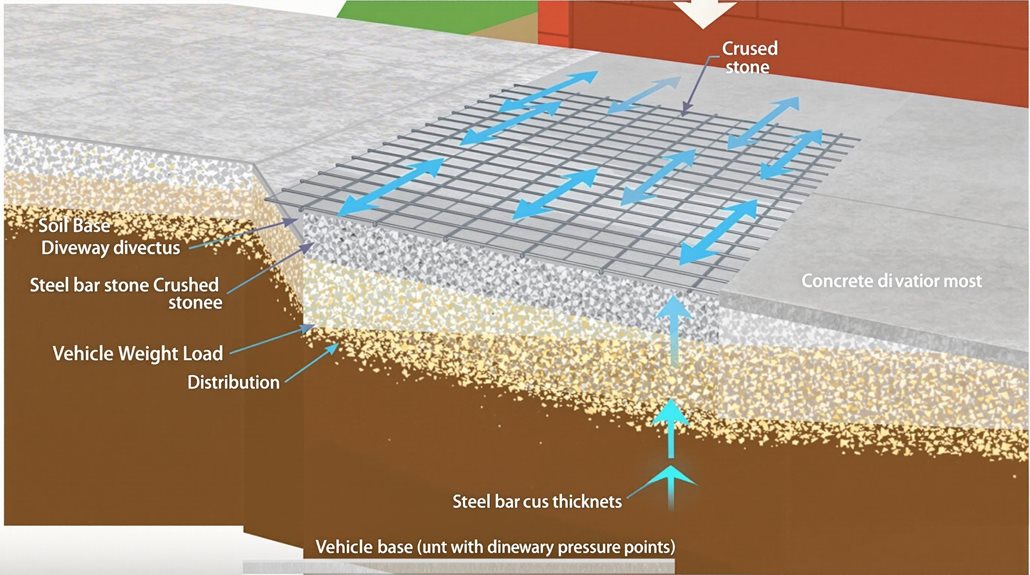
When determining appropriate concrete driveway thickness, multiple critical factors must be carefully evaluated through engineering calculations and site-specific assessments.
The soil bearing capacity, measured in pounds per square foot (psf), serves as a fundamental consideration that directly influences the required thickness of the concrete slab.
Environmental conditions, including freeze-thaw cycles and moisture exposure, greatly impact the necessary driveway thickness, particularly in regions experiencing extreme temperature variations.
The anticipated traffic load, comprising both frequency and weight of vehicles, determines the structural requirements of the concrete.
Additional factors include drainage patterns, soil composition, and reinforcement methods selected.
The presence of heavy equipment, such as RVs or commercial vehicles, requires increased thickness specifications, typically ranging from 5 to 8 inches, compared to standard residential applications of 4 inches.
Quality sealers are essential for protecting concrete driveways and extending their lifespan beyond 25 years when properly maintained.
Soil Testing and Site Preparation Guidelines
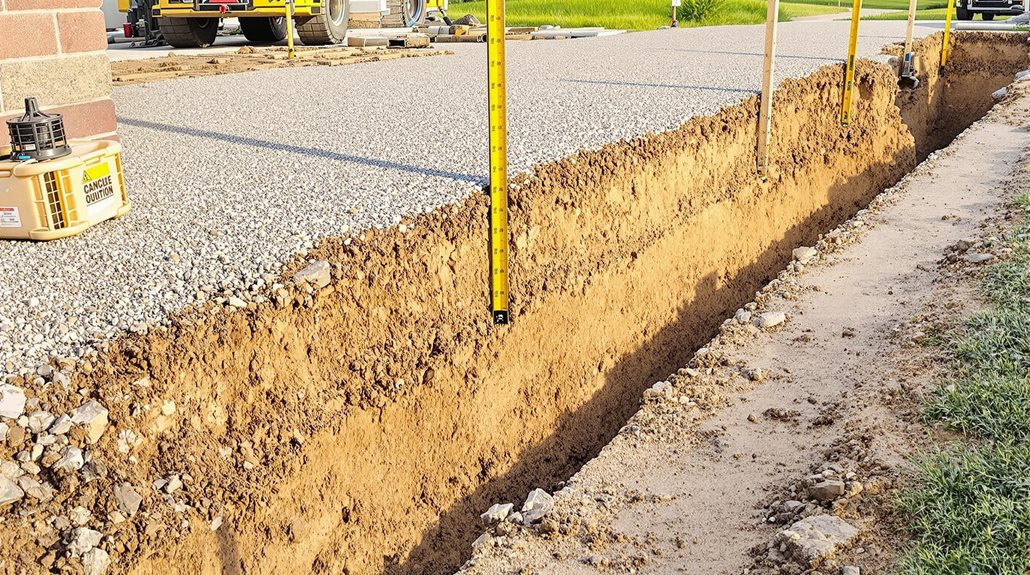

Proper evaluation of soil conditions through thorough testing forms the foundation for successful concrete driveway installation, building upon the thickness considerations previously discussed.
Professional contractors employ soil core sampling and load-bearing capacity tests to determine the subgrade's stability, composition, and drainage characteristics.
The site preparation process begins with removing organic material and existing fill to reach stable native soil.
Contractors then conduct soil compaction tests using a nuclear densimeter or proctor test to achieve a minimum 95% compaction rate. Areas with clay soils or poor drainage often require additional base preparation, including 4-6 inches of compacted gravel aggregate.
A proper moisture barrier and reinforcement grid installation follows soil preparation, preventing water migration and soil settlement that could compromise the driveway's structural integrity.
These preparatory steps guarantee ideal load-bearing capacity and longevity of the concrete installation.
With quality assurance standards upheld by certified teams, proper site preparation ensures projects meet both residential and commercial property requirements.
Climate and Environmental Impact on Concrete Specifications
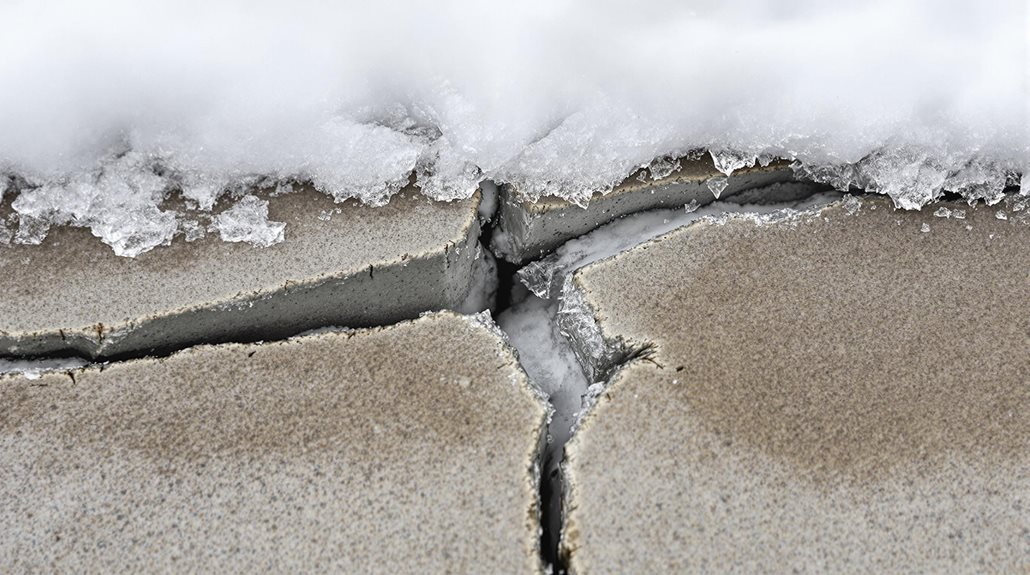

Climate conditions greatly influence concrete driveway specifications, with factors like temperature extremes, freeze-thaw cycles, and precipitation patterns determining ideal mix designs and installation requirements.
In cold regions experiencing frequent freeze-thaw cycles, air-entrained concrete mixtures containing 5-7% air content help prevent surface scaling and internal cracking.
Hot climates necessitate specific curing procedures and concrete admixtures to control setting times and prevent rapid moisture loss.
Contractors must adjust water-cement ratios based on local humidity levels, typically maintaining a ratio between 0.40 and 0.45 for peak strength and durability.
Achieving optimal concrete performance requires precise water-cement ratios of 0.40-0.45, carefully balanced according to ambient humidity conditions.
Additionally, exposure to deicing chemicals in snow-prone areas requires increasing the concrete's compressive strength to 4,500 PSI or higher, while incorporating chemical-resistant sealers to protect against deterioration.
Working with certified concrete experts ensures proper mix selection and installation techniques for your specific climate conditions.
Reinforcement Options for Enhanced Load-Bearing Capacity
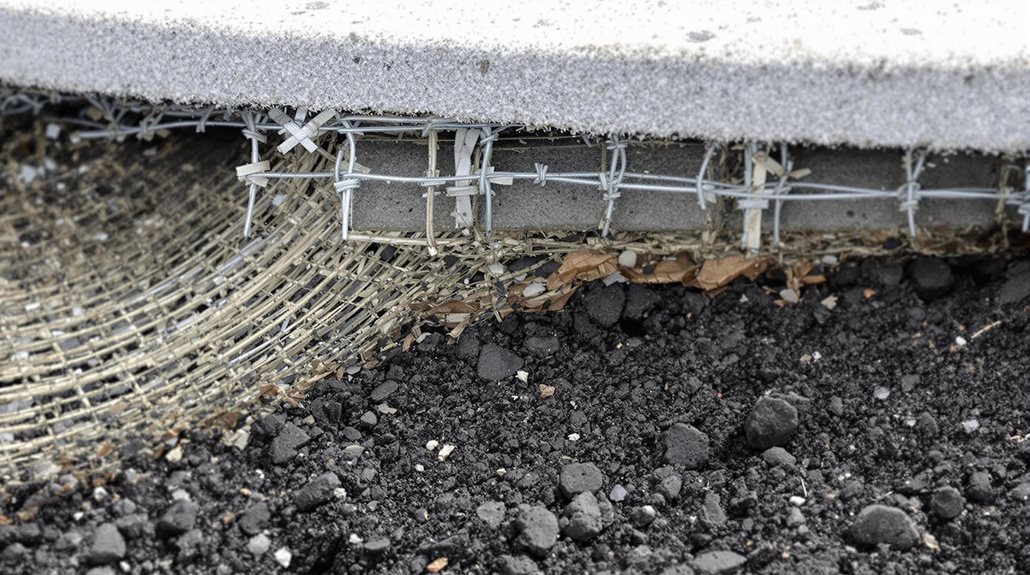

Several reinforcement options exist for concrete driveways to enhance their load-bearing capacity and structural integrity over time. The most common method involves steel rebar placement, typically using #3 or #4 bars in a grid pattern spaced 12 to 18 inches apart, which provides tensile strength and crack resistance.
Wire mesh reinforcement offers a cost-effective alternative, utilizing 6×6 inch welded wire fabric that distributes loads evenly across the concrete surface.
For enhanced performance, fiber reinforcement technology incorporates synthetic or steel fibers throughout the concrete mix, providing multidirectional strength enhancement.
Post-tensioning systems, though less common in residential applications, utilize high-strength steel cables under tension to create compression forces within the concrete, markedly increasing load capacity while reducing the likelihood of cracking and settlement issues.
With proper installation from certified concrete experts, these reinforcement methods can help concrete driveways last up to 30 years with minimal maintenance requirements.
Maintenance Practices to Preserve Structural Integrity
Regular maintenance protocols for concrete driveways serve as a critical defense against structural deterioration, helping to maximize the material's load-bearing capabilities throughout its service life.
Property owners should implement a thorough maintenance schedule that includes annual sealing, prompt crack repair, and periodic surface cleaning.
Protective sealants should be applied every 2-3 years to prevent water infiltration and chemical damage, while surface cracks exceeding 1/8 inch require immediate patching with appropriate concrete repair compounds.
Regular application of sealants and swift repair of surface cracks are essential safeguards against water damage in concrete driveways.
Regular pressure washing removes harmful substances like oil, road salt, and organic debris that can compromise structural integrity.
Professional inspection of control joints, expansion gaps, and drainage patterns should occur annually, particularly in regions experiencing freeze-thaw cycles.
These evaluations help identify potential issues before they impact the driveway's load-bearing capacity or require costly structural repairs.
Expert craftsmanship ensures that maintenance needs are minimized through proper initial installation techniques and material selection.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Should I Wait Before Parking on a Newly Poured Driveway?
One should wait at least 7 days before parking passenger vehicles and 28 days for heavy vehicles on newly poured concrete driveways to guarantee proper curing and strength.
Can I Pour Concrete Directly Over My Existing Damaged Concrete Driveway?
Pouring concrete over damaged concrete isn't recommended, as it can lead to bonding issues and future cracking. Most professionals suggest removing the old driveway before installing a new one.
What Type of Surface Finish Is Best for Preventing Tire Marks?
A broom-finished or textured concrete surface provides excellent traction while minimizing tire marks. Many homeowners also choose exposed aggregate finishes, which naturally conceal rubber transfer from vehicles.
How Much Does Temperature Affect Concrete Curing Time for Driveways?
Temperature considerably influences concrete curing time. Warmer conditions accelerate the process, with ideal temperatures between 50-85°F. Every 20°F increase roughly doubles the curing speed for driveways.
Should Expansion Joints Be Sealed Immediately After the Concrete Has Cured?
Experienced contractors recommend waiting 28-90 days before sealing expansion joints, allowing concrete to fully cure and settle. Early sealing can trap moisture and affect joint performance.
Expert Final Thougts
Proper concrete driveway design requires careful consideration of load capacity requirements, thickness specifications, soil conditions, and environmental factors. Through appropriate materials selection, reinforcement methods, and installation practices, driveways can be engineered to safely handle expected vehicle weights while resisting deterioration. Regular maintenance, including sealing and crack repair, helps preserve structural integrity, ensuring driveways maintain their load-bearing capacity throughout their service life.
